At physiological maturity fruit have accumulated a range of complex molecules in the form of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and organic acids.
Ripening and respiration Ripening is a term applied to fruit that describes the transition from physiological maturity to senescence (ageing and death of the plant tissues).. Ethylene gas filled in pressurized cans promote fruit ripening in 24-48 Acts as an artificial ripening.. In 1901 Neljubow identified the active component of the gas to be ethylene but it was not until 1934 that Gane identified that plants could synthesise ethylene and in 1935 Crocker proposed ethylene to be the hormone responsible for fruit ripening and senescence of vegetative tissues.
Fruit ripening gas - ethylene Ethylene (C 2H 4, also known as ethene) is a gaseous organic compound that is the simplest of the alkene chemical structures (alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond). Ftp Client For Mac Free Download
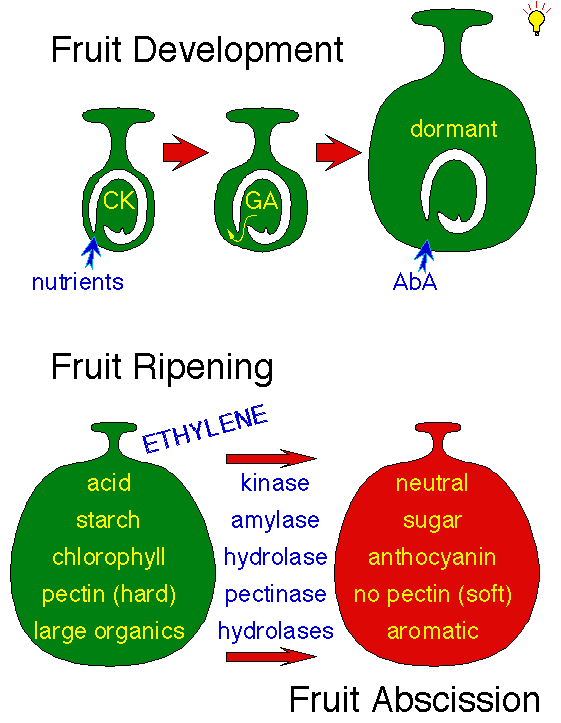


Understanding the fundamental relationship between ethylene and fruit respiration rates during ripening is necessary in order to manage the harvesting, storage and distribution processes.. ARTIFICIAL RIPENING OF FRUITS BY ETHYLENE Download PDF Full The ethylene produced by the injured fruit tissue triggers a broader ripening response.. Ethylene also plays a role in response to water stress, chilling and mechanical injury.. Ripening is the start of significant biochemical and physiological transformations, such as changes in skin colour, internal flesh softening, aroma development and sweetening.. Considerable research has since been conducted into the effects of ethylene on fruit ripening. ae05505a44


0